June 3, 2015
Clark Gascoigne, +1 202 293 0740 ext. 222

Illicit Financial Flows Have “Outsized Impact on Poorest Countries”
FfD Negotiators Urged to Target Illicit Financial Flows and Trade Misinvoicing
WASHINGTON, DC – Illicit financial flows (IFFs), stemming from crime, corruption, and tax evasion, have an outsized impact on the world’s poorest countries, according to a new study released today by Global Financial Integrity (GFI), a Washington, DC-based research and advisory organization. Titled “Illicit Financial Flows and Development Indices: 2008–2012,” the report also finds strong correlations between higher illicit outflows and higher levels of poverty and economic inequality.
 “Illicit financial flows have an outsized impact on the poorest countries in the world,” said Tom Cardamone, GFI’s managing director. “The value of this study is that it goes beyond ‘the big number’ of cumulative global illicit outflows and focuses instead on the impact of IFFs in the poorest of places. A lot of attention gets paid to the massive amount of illicit money flowing out of China, Russia, and other major emerging markets. However, on a relative basis, when you compare illicit financial flows to major development indices like GDP, FDI, and total trade, it becomes extremely clear that illicit outflows take a particularly devastating toll on the world’s poorest economies.”
“Illicit financial flows have an outsized impact on the poorest countries in the world,” said Tom Cardamone, GFI’s managing director. “The value of this study is that it goes beyond ‘the big number’ of cumulative global illicit outflows and focuses instead on the impact of IFFs in the poorest of places. A lot of attention gets paid to the massive amount of illicit money flowing out of China, Russia, and other major emerging markets. However, on a relative basis, when you compare illicit financial flows to major development indices like GDP, FDI, and total trade, it becomes extremely clear that illicit outflows take a particularly devastating toll on the world’s poorest economies.”
Authored by GFI Junior Economist Joseph Spanjers and GFI Economics Fellow Håkon Frede Foss, the report compares illicit outflows from the world’s poorest economies to some traditional indicators of development—including GDP, total trade, official development assistance plus foreign direct investment, public expenditures on education and health services, and total tax revenue, among others—for the years 2008–2012, the most recent five-year period for which data are currently available.
“For nearly one-quarter of the 82 countries that we analyzed, the ratio of illicit financial outflows to GDP is ten percent or greater,” commented Mr. Spanjers, the principal author of the report. “For example, IFFs to GDP amount to a staggering 21.7 percent in Honduras, 18.1 percent in Zambia, and 11.2 percent in Ethiopia. It would not be overstating the point to note that, if any other economic factor had a double-digit ratio to GDP, it would be front-page news. Unfortunately, this is often not the case when illicit flows are concerned.”
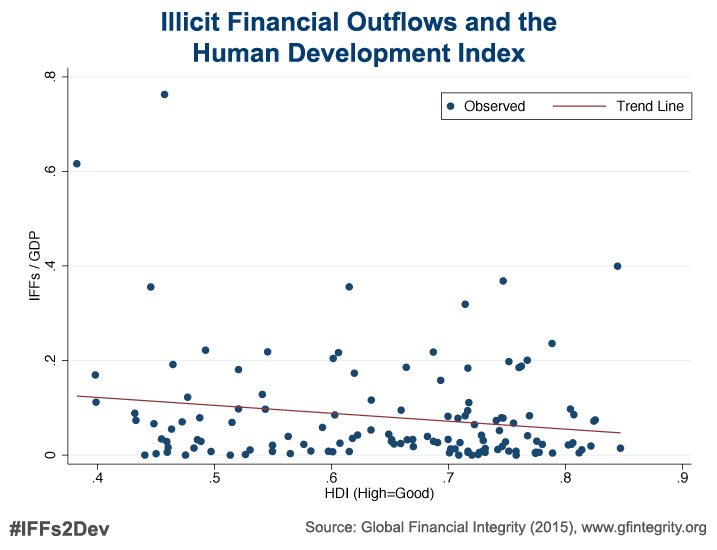 The authors additionally find a disturbing correlation between illicit financial flows and 1) higher levels of poverty, 2) higher levels of economic inequality, 3) and lower levels of human development, as measured by the United Nations’ annual Human Development Index.
The authors additionally find a disturbing correlation between illicit financial flows and 1) higher levels of poverty, 2) higher levels of economic inequality, 3) and lower levels of human development, as measured by the United Nations’ annual Human Development Index.
“Higher illicit outflows aggravate poverty, exacerbate income inequality, and erode human development in the world’s poorest countries,” added Mr. Spanjers.
Additional correlations are found between higher relative levels of illicit financial flows and trade openness, tariff rates, and the efficiency of customs.
Policy Recommendations
The report lays out several policy recommendations, and puts a particular emphasis on the outcome of next month’s Third Financing for Development (FfD) Conference in Addis Ababa.
“Concerted action is needed by the international community to assist all developing nations in curtailing the phenomenon of ‘trade misinvoicing’ (i.e. trade fraud) which moves up to 80 percent of all illicit funds offshore,” said Mr. Cardamone, GFI’s managing director, who is leading the organization’s work on the FfD process. “As world leaders continue to negotiate the outcome of next month’s Financing for Development Conference, curtailing trade misinvoicing must be a focus given its link to domestic resource mobilization.”
“We look forward to a robust agreement that: 1) mandates the IMF to regularly measure trade misinvoicing levels from all developing countries; 2) commits the world community to halve trade misinvoicing in all developing countries by 2030; and 3) requires donor countries to provide financing for trade pricing databases and training in customs departments so poor nations can stop misinvoiced goods before they leave the ports. It’s simply impossible to produce a credible FfD Outcome Document that doesn’t commit to measuring and reducing trade misinvoicing by an explicit percentage,” added Mr. Cardamone.
Funding
Funding for the new report, “Illicit Financial Flows and Development Indices: 2008–2012,” was generously provided by the Government of Finland.
###
Notes to Editors:
- Click here for an HTML version of this press release.
- More information about the GFI report—including Excel files with the report’s data—is available on the GFI website here. A PDF of the full report can be downloaded here [PDF | 2 MB].
- To schedule an interview with Mr. Cardamone or Mr. Spanjers, contact Clark Gascoigne at [email protected] / +1 202 293 0740, ext. 222 (Office) / +1 202-815-4029 (Mobile). On-camera spokespersons are available in Washington, DC.
- Global Financial Integrity (GFI) is a Washington, DC-based research and advisory organization, which promotes transparency in the international financial system as a means to global development.
- Please use the #IFFs2Dev hashtag on Twitter and social media to discuss the report.
Journalist Contact:
Clark Gascoigne
Global Financial Integrity
[email protected]
+1 202-293-0740 ext. 222

